Oracle Compute Cloud Service Overview – Network
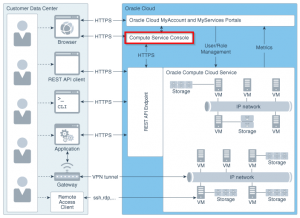
Oracle Compute as part of Oracle Cloud Service, is a standards-based infrastructure service. In Network section we control the ways of how we can connect to our Oracle Cloud Services.
Access to Oracle Compute instances is possible in several ways.
We can use a web browser to access the web console, we can access the REST API directly, or we can use the command-line interface. Secure access is provided by protocols such as SSH and RDP. We can also set up a VPN tunnel to provide secure access to instances in our Oracle Compute Cloud Service network.
Here is a brief description of all Oracle Cloud Compute Network dashboard:
Shared Network
| Security Rules | Here we control network access between our instances and the Internet. We can create, view, update, and delete security rules. |
| Security Lists | A set of instances that we can specify as a source or destination in security rules. |
| Security Applications | A protocol-type and port mapping, which we can define and then use in security rules to control traffic to/from instances. |
| Security IP Lists | A group of IP addresses or subnets that can be used in security rules. |
| IP Reservations | We can reserve public IP addresses for instances that require network access to the internet. |
IP Network
| IP Networks | Allows us to define an IP subnet in our account. The size of the IP subnet and the IP addresses in the subnet are determined by the IP address prefix that we specify while creating the IP network |
| IP Exchanges | Enables communication between IP networks that have non-overlapping addresses |
| Virtual NIC Sets | A collection of one or more virtual network interface controllers (vNIC). These vNIC sets are used to specify the next hop address in a route. |
| Routes | A route specifies the IP address of the destination as well as a vNIC set which provides the next hop for routing packets to the specified destination. If there are multiple routes to a destination, the route with the lowest administrative distance is used. |
| Security Rules | To control network access between our instances and the Internet. Here we can create, view, update, and delete security rules. |
| Access Control Lists | (ACL) is a collection of security rules. After we create an ACL, we can add multiple security rules to it. We can then apply each ACL to one or more vNIC sets. |
| Security Protocols | Specify a transport protocol and the source and destination ports to be used with each protocol. We can use security protocols in security rules, to determine the type of traffic that is permitted by each security rule. |
| IP Address Prefix Sets | It contains a list of IP addresses in the Classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) address prefix format. When we create a security rule, we can specify a list of IP address prefix sets as the source or destination for permitted traffic. |
| IP Reservations | Here we can reserve public IP addresses for instances in IP networks that require network access to the internet. |
VPN
| VPN Gateways | Allows us to create a VPN connection between our data center and our Oracle Compute Cloud Service instances. Here we can view and manage our VPN gateway instances. |
| Customer Devices | We can establish a VPN connection between a VPN gateway and a third-party VPN device in our data center. |
| Connections | A list of connections between Oracle Cloud VPN gateways and third-party VPN gateways in our data center. We can only create and manage partnerships between Oracle Cloud VPN gateways and device gateways in our data center. To create and manage partnerships between Oracle Cloud VPN gateways and Corente Services Gateways in our data center we use the App Net Manager. |
SSH Public Keys – We can use SSH keys to enable secure access to our instances.
Source: http://docs.oracle.com/cloud